Energy
HYDROPOWER IN SPAIN
Hydroelectricity is the electric energy generated using the potential energy of flows of water
This industrial sector has a unique importance from the point of view of water resources, as it takes a massive inflow of water in quantities not comparable to other industrial activities in which the water is a resource.
Spainis a country relatively rich in hydropower resources that traditionally have been used to satisfy the demand.
The hydroelectric development in our country, began in the fifties and reached it´s maximum growth in the seventies, decreasing by the economic regime applied to the rates.
Advantages
- Renewable Energy
- Power that is not necessary to import
- Does not need refrigeration or boiler, which reduces the cost
- No pollution
- Allow the water storage
- Used to regulatethe river flow when entails the construction of a dam
- Dam constructionalso brings recreation usages
Disadvantages
- Depends on rainfall
- It is necessary an abundant fluvial current and a injured orography
- It maybe necessary to build infrastructure to conduct electricity
- Changesin ecosystems
- Social ordemographic problems
- Lossof water quality
Hydroelectric generation in Spain
Renewableenergy generation is subject to meteorological conditions but in Spain the trend is positive.
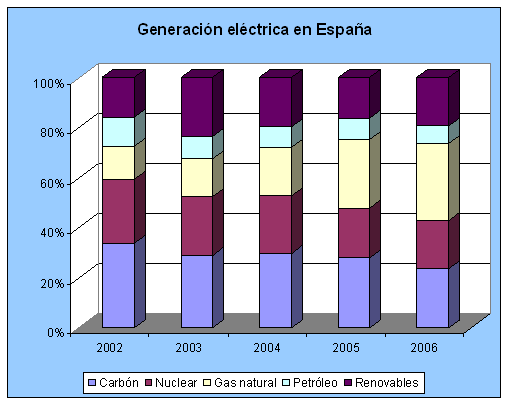
Figure1. Electric Power Generation. Source: Environmental Profile of Spain 2007
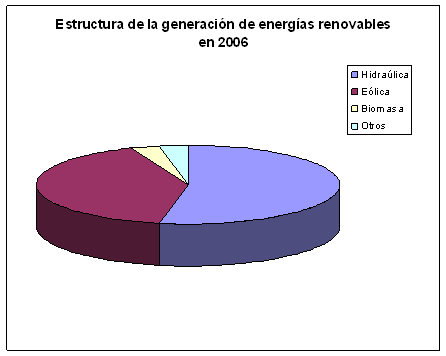
Figure 2. Renewable Energies. Source: Environmental Profile of Spain 2007
Thedata collected in 2004 interms of power installed by Autonomous Communities reflect a higher production in Catalonia, Andalusia, Galicia, Castilla y León, Aragón and Navarra, as is shown in the following graph, in terms of production of minihydraulics plants. In contrast, the regions with more hydroelectric power installed in hydroelectric plants of 10-50 MW are Catalonia, Aragon and Galicia.
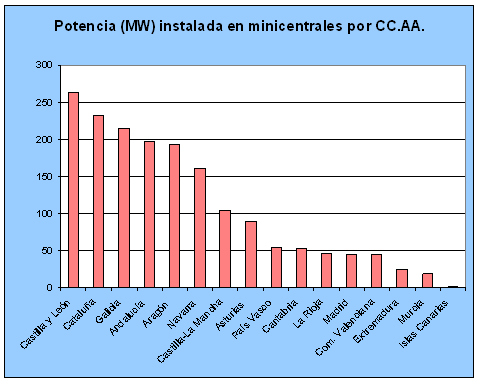
Figure 3. Mini-power stations
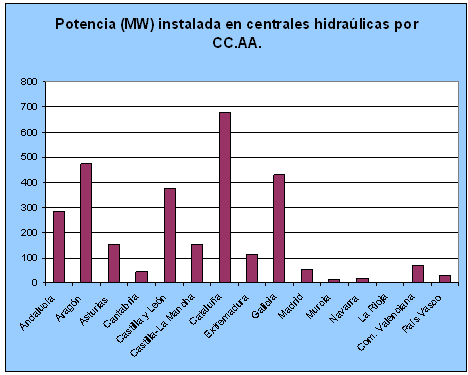
Figure 4. Power stations
Number of hydroelectric projects on river basin district and power installed.
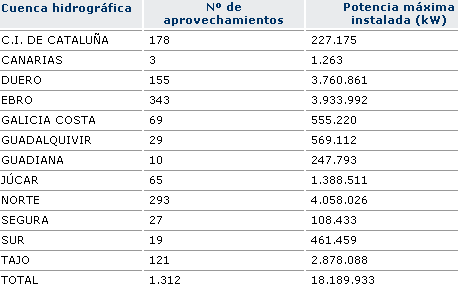
Table1. Hydroelectric Exploitation. Source: Integrated Water Information System
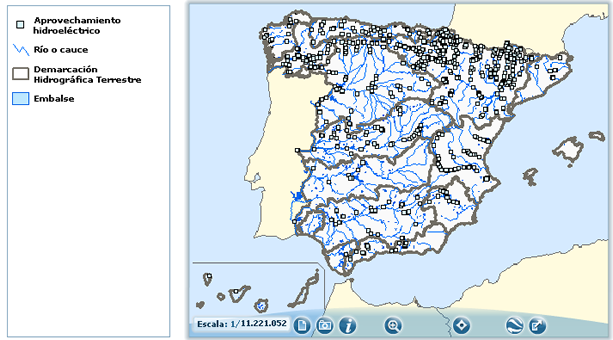
Figure1. Hydroelectric map. Source: Sistema Integrado de Información del Agua. SIA
Environmental Impact
The hydraulic energy is not a totally clean energy, because it must consider the environmental impact associated with the prey construction. According to the IHA it is necessary to consider nine key aspects to maintain the hydraulic potential with a sustainable development.
- Water quality
- Erosion and sediments transport
- Hydrology and environmental flows of the rivers
- Endemic species and endangered
- Passage of species
- Animals and vegetals plagues in the dams
- Sanitary aspects
- Activities of construction
- Systems of water management
Demand and future evolution
The physical limitations mentioned and the costs of possible new infrastructures make suppose that the hydroelectric growth in the next years will be small. The National Power Plan of 1991 anticipated an increase of 900 MW for the year 2000 in average and great hydroelectric power stations and of 800MW in mini-power stations. Other estimations more optimistic consider that the power installed in 7.000 MW in 20 years could be increased, in case the State would foment this type of energy.
SOME DATA ABOUT ENERGY IN SPAIN
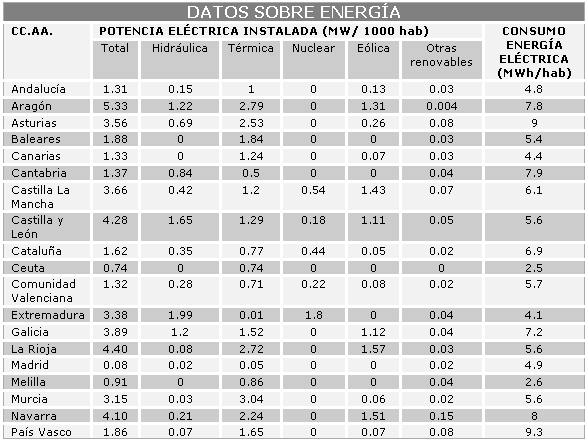
Table2. Data on energy in Spain. Source: Environmental Profile ofSpain 2007